| Product: | Adenosine | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalog Number: | 17321 | ||||||||
| CAS Number: | 58-61-7 | ||||||||
| Synonyms: | 9-β-D-Ribofuranosyladenine; Adenine riboside; Adenine-9-β-D-ribofuranoside | ||||||||
| Pricing: |
|
||||||||
| Formula: | C10H13N5O4 | ||||||||
| Chemical Purity: | >99% | ||||||||
| Molecular Weight: | 267.24 | ||||||||
| Structure: |
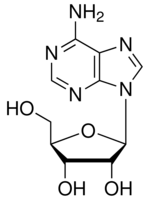
|
||||||||
| Appearance: | White solid | ||||||||
| Category: | Anti-cancer compounds | ||||||||
| Stability: | Stable under recommended storage conditions. | ||||||||
| Storage: |
Keep container tightly closed in a dry and well-ventilated place. Recommended storage temperature: 2-8°C. |
||||||||
| Transportation: |
Non-hazardous for transport |
||||||||
| Literature References: |
Liu, X., et al., Induction Of Cell Cycle Arrest At G1 And S Phases And CAMP-dependent Differentiation In C6 Glioma By Low Concentration Of Cycloheximide. BMC Cancer 10, 684, (2010); Díez-Zaera, M., et al., Tissue-nonspecific Alkaline Phosphatase Promotes Axonal Growth Of Hippocampal Neurons. Molecular Biology of the Cell 22, 1014-24, (2011); Hutchinson, S.A., and Scammells, P.J., A1 adenosine receptor agonists: medicinal chemistry and therapeutic potential. Curr. Pharm. Des. 10, 2021-2039, (2004); Fredholm, B.B., et al., Actions of Adenosine at Its Receptors in the CNS: Insights from Knockouts and Drugs. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. 27, (2004); Livingston, M., et al., Adenosine, inflammation and asthma--a review. Inflamm. Res. 53, 171-178, (2004); Sullivan, G.W., Adenosine A2A receptor agonists as anti-inflammatory agents. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 4, 1313-1319, (2003); Rorke, S., and Holgate, S.T., Targeting adenosine receptors: novel therapeutic targets in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Med. 1, 99-105, (2002); Merck 14,153; Beil. 26,IV,3598; FT-IR 1 (2), 720:A / FT-IR 2 (3), 3684:C / FT-NMR 1 (3), 222:A / IR-Spectra (3), 1296:E / IR-Spectra (2), 1128:F / NMR-Reference 2 (2), 597:C / RegBook 1 (2), 2475:K / Sax 6, 138 / Sigma FT-IR 1 (1), 752:C / Structure Index 1, 391:A:6 |
||||||||
| MSDS: | |||||||||
| Description: |
Endogenous neurotransmitter at adenosine receptors. Cardioprotective effects may relate to activation of A1 adenosine receptors. The antiplatelet and anti−inflammatory actions of adenosine appear to be mediated via the A2 adenosine receptor. In contrast, adenosine appears to be a pro-inflammatory mediator in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). |
