| Product: | Irinotecan hydrochloride | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalog Number: | 17532 | ||||
| CAS Number: | 100286-90-6 | ||||
| Synonyms: |
(S)-4,11-diethyl-3,4,12,14-tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-3,14-dioxo-1H-pyrano[3’,4’:6,7]indolizino[1,2-b]quinolin-9-yl ester; [1,4’-Bipiperidine]-1’-carboxylic acid; CPT-11 |
||||
| Pricing: |
|
||||
| Formula: | C33H38N4O6 • HCl | ||||
| Molecular Weight: | 623.14 | ||||
| Structure: |
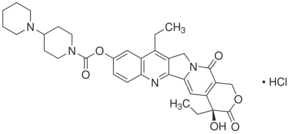
|
||||
| Appearance: | Solid | ||||
| Category: | Anti-cancer compounds | ||||
| Stability: | Stable under recommended storage conditions | ||||
| Storage: |
Keep container tightly closed in a dry and well ventilated place. Recommended storage temperature: 2-8°C. |
||||
| Transportation: |
Non-hazardous for transport |
||||
| Literature References: |
Illum, H., Irinotecan and radiosensitization in rectal cancer (Epub ahead of print) Anticancer Drug Des., (2010); Ma, M.K., and McLeod, H.L., Lessons learned from the irinotecan metabolic pathway. Curr. Med. Chem. 10, 41-49, (2003); Lin CP, Ban Y, Lyu YL, Liu LF., Proteasome-dependent processing of topoisomerase I-DNA adducts into DNA double strand breaks at arrested replication forks. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 28084-28092, (2009); Crea F, Giovannetti E, Cortesi F, et. al., Epigenetic mechanisms of irinotecan sensitivity in colorectal cancer cell lines. Mol. Cancer Ther. 8, 1964-1973, (2009); Barth SW, Briviba K, Watzl B, et. al., In vivo bioassay to detect irinotecan-stabilized DNA/topoisomerase I complexes in rats. Biotechnol. J. 5, 321-327, (2010); Bandyopadhyay K, Gjerset RA., Protein kinase CK2 is a central regulator of topoisomerase I hyperphosphorylation and camptothecin sensitivity in cancer cell lines. Biochemistry 50, 704-714, (2011); Illum, H., Irinotecan and radiosensitization in rectal cancer (Epub ahead of print) Anticancer Drug Des. 22, 324-329, (2011); Mathijssen, R.H., et al., Pharmacology of topoisomerase I inhibitors irinotecan (CPT-11) and topotecan. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2, 103-123, (2002); Tallman, M.N., et al., The contribution of intestinal UDP-glucuronosyltransferases in modulating 7-ethyl-10-hydroxy-camptothecin (SN-38)-induced gastrointestinal toxicity in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 320, 29-37, (2007); Ma, M.K., and McLeod, H.L., Lessons learned from the irinotecan metabolic pathway. Curr. Med. Chem. 10, 41-49, (2003); Vallbohmer, D., et al., Molecular determinants of irinotecan efficacy. Int. J. Cancer 119, 2435-2442, (2006); Merck 14,5091 |
||||
| MSDS: | |||||
| Description: |
The anticancer agent, irinotecan, is a prodrug that is converted by tissue carboxylesterase to 7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin (SN-38), a potent inhibitor of DNA topoisomerase I. Its action is terminated by glucuronidation by UDP glucuronosyl transferase 1A1 (UGT1A1). It proves useful in radiation treatment of tumors by sensitizing tissue to radiation damage. The anticancer agent, irinotecan, is a prodrug that is converted by tissue carboxylesterase to 7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin (SN-38), a potent inhibitor of DNA topoisomerase I. Its action is terminated by glucuronidation by UDP glucuronosyl transferase. |
