| Product: | Tamoxifen | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalog Number: | 13631 | ||||||||
| CAS Number: | 10540-29-1 | ||||||||
| Synonyms: |
(Z)-2-[4-(1,2-Diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy]-N,N-dimethylethanamine; Trans-2-[4-(1,2-Diphenyl-1-butenyl)phenoxy]-N,N-dimethylethylamine |
||||||||
| Pricing: |
|
||||||||
| Formula: | C26H29NO | ||||||||
| Chemical Purity: | >99% | ||||||||
| Molecular Weight: | 371.51 | ||||||||
| Structure: |
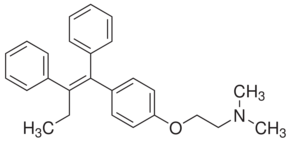
|
||||||||
| Appearance: | Solid | ||||||||
| Category: | Protein Kinase Inhibitors and Activators | ||||||||
| Stability: | Stable under recommended storage conditions. | ||||||||
| Storage: |
Keep container tightly closed in a dry and well-ventilated place. Storage temperature: 2-8°C. Light sensitive |
||||||||
| Transportation: |
Non-hazardous for transport |
||||||||
| Literature References: |
Mandlekar S, and Kong AN., Mechanisms of tamoxifen-induced apoptosis Apoptosis 6, 469-477, (2001); de Médina P, et al., Multiple targeting by the antitumor drug tamoxifen: a structure-activity study Curr. Med. Chem. Anticancer Agents 4, 491-508, (2004); Nabha SM, et al., Upregulation of PKC-δ contributes to antiestrogen resistance in mammary tumor cells Oncogene 24, 3166-3176, (2005); Lin X, et al., Overexpression of PKCα is required to impart estradiol inhibition and tamoxifen-resistance in a T47D human breast cancer tumor model Carcinogenesis 27, 1538-1546, (2006); Frankel LB, et al., Protein kinase Cα is a marker for antiestrogen resistance and is involved in the growth of tamoxifen resistant human breast cancer cells Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 104, 165-179, (2007); Hurtado A, et al., Regulation of ERBB2 by oestrogen receptor-PAX2 determines response to tamoxifen Nature 456, 663-666, (2008); Sengupta S, and Jordan VC., Selective estrogen modulators as an anticancer tool: mechanisms of efficiency and resistance Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 630, 206-219, (2008); Wang, D., et al., Cardiomyocyte Cyclooxygenase-2 Influences Cardiac Rhythm And Function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106, 7548-52, (2009); Thorel, F., et al., Conversion Of Adult Pancreatic Alpha-cells To Beta-cells After Extreme Beta-cell Loss. Nature 464, 1149-54, (2010); Wicksteed, B., et al., Conditional Gene Targeting In Mouse Pancreatic {beta}-Cells: Analysis Of Ectopic Cre Transgene Expression In The Brain. Diabetes 59, 3090-8, (2010); Liu, Y., et al., Tamoxifen-independent Recombination In The RIP-CreER Mouse. PLoS ONE 5, e13533, (2010); Saunders, T.L., Inducible Transgenic Mouse Models. Methods Mol. Biol. 693, 103-15, (2011); Friedel, R.H., et al., Generating Conditional Knockout Mice. Methods Mol. Biol. 693, 205-31, (2011); Feng, J., et al., Dual Origin Of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Contributing To Organ Growth And Repair. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108, 6503-8, (2011); Georgala, P.A., et al., The Generation Of Superficial Cortical Layers Is Regulated By Levels Of The Transcription Factor Pax6. Cereb. Cortex 21, 81-94, (2011); Issandou, M., et al., Opposite effects of tamoxifen on in vitro protein kinase C activity and endogenous protein phosphorylation in intact MCF-7 cells. Cancer Res. 50, 5845-5850, (1990); O'Brian, C.A., et al., Inhibition of protein kinase C by tamoxifen. Cancer Res. 45, 2462-2465, (1985); Gold, E., et al., Tamoxifen and norethisterone: effects on plasma cholesterol and total body calcium content in the estrogen-deficient rat. Horm. Metab. Res. 26, 100-103, (1994); Pienta, K.J., et al., Inhibition of prostate cancer growth by vinblastine and tamoxifen. Prostate 26, 270-274, (1995); Edwards, K.J., et al., A molecular modeling study of the interactions between the antiestrogen drug tamoxifen and several derivatives, and the calcium-binding protein calmodulin. J. Med. Chem. 35, 2753-2761, (1992); Powis, G., Signalling targets for anticancer drug development. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 12, 188-194, (1991); Wiseman, H., Tamoxifen and estrogens as membrane antioxidants: comparison with cholesterol. Meth. Enzymol. 234, 590-602, (1994); Merck 14,9048; Corp MSDS 1 (1), 1454:A / FT-IR 2 (2), 2153:D / FT-NMR 1 (2), 575:B / RegBook 1 (1), 1469:F / Structure Index 1, 229:A:7 |
||||||||
| MSDS: | |||||||||
| Description: |
Tamoxifen is a selective estrogen response modifier (SERM), protein kinase C inhibitor and anti-angiogenetic factor. Tamoxifen is a prodrug that is metabolized to active metabolites 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT) and endoxifen by cytochrome P450 isoforms CYP2D6 and CYP3A4. In breast cancer, the gene repressor activity of tamoxifen against ERBB2 is dependent upon PAX2. Blocks estradiol-stimulated VEGF production in breast tumor cells. |
||||||||
| Applications: |
Protein kinase C inhibitor. Induces apoptosis in human malignant glioma cell lines. Tamoxifen and its metabolite 4-hydroxytamoxifen are selective estrogen response modifiers (SERMs) that act as estrogen antagonists in mammary gland. Blocks estradiol-stimulated VEGF production in breast tumor cells |
