| Product: | Bleomycin Sulfate | |
|---|---|---|
| Catalog Number: | 17386 | |
| CAS Number: | 9041-93-4 | |
| Synonyms: |
Bleomycin sulfate; Blenoxane; Blexane; Bleo |
|
| Pricing: |
|
|
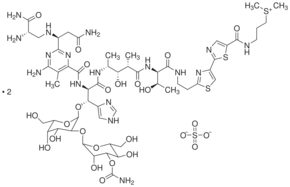
| Formula: | C55H84N17O21S3 • H2SO4 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 1415.6 | |
| Structure: |
|
|
| Appearance: | Crystalline | |
| Category: | Anti-cancer compounds | |
| Stability: | Stable under recommended storage conditions. | |
| Storage: |
Keep container tightly closed in a dry and well-ventilated place. Recommended storage temperature: 2-8°C. Strongly hygroscopic |
|
| Transportation: |
Non-hazardous for transport |
|
| Literature References: |
Huttenhofer, A., et al., Cleavage of tRNA by Fe(II)-bleomycin. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 24471-24475, (1992); Holmes, C.E, et al., Fe bleomycin as a probe of RNA conformation. Nucleic Acids Res. 24, 3399-3406, (1996); Maggliozzo, R.S, et al., Transfer RNA is cleaved by activated bleomycin. Mol. Pharmacol. 35, 428-432, (1989); Morgan, M.A. and Hecht, S.M., Iron (II) bleomycin-mediated degradation of a DNA-RNA heteroduplex. Biochemistry 33, 10286-10293, (1994); Hamilton, R.F., et al., Bleomycin induces apoptosis in human alveolar macrophages. Am. J. Physiol. 26, L318-L325, (1995); Mir, L.M., et al., Bleomycin: revival of an old drug. Gen. Pharmacol. 27, 745-748, (1996); Sam, J.W., et al., Sequence-specific changes in the metal site of ferric bleomycin induced by the binding of DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 16090-16097, (1998); Holmes, C.E, et al., On the chemistry of RNA degradation by Fe bleomycin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 5, 1235-1248, (1997); Vernole, P, et al., Induction of apoptosis by bleomycin in resting and cycling human lymphocytes. Mutagenesis 13, 209-215, (1998); Christensen, J.G., et al., Regulation of apoptosis in mouse hepatocytes and alteration of apoptosis by nongenotoxic carcinogens. Cell. Growth Differ. 9, 815-825, (1998); Araki, T, et al., Changes in c-Jun but not Bcl-2 family proteins in p53-dependent apoptosis of mouse cerebellar granule neurons induced by DNA damaging agent bleomycin. Brain Res. 794, 239-247, (1998); Kross, J, et al., Specificity of deoxyribonucleic acid cleavage by bleomycin, phleomycin and tallysomycin. Biochemistry 21, 4310-4318, (1982); Kross, J, et al., Structural basis for the deoxyribonucleic acid affinity of bleomycins. Biochemistry 21, 3711-3721, (1982); Carter, B.J, et al., Site-specific cleavage of RNA by Fe(II) bleomycin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 87, 9373-9377, (1990); Schirner, M., et al., Antiangiogenic chemotherapeutic agents: characterization in comparison to their tumor growth inhibition in human renal cell carcinoma models. Clin. Cancer Res. 4, 1331-1336, (1998); Merck 14,1318 |
|
| MSDS: | ||
| Description: |
An antineoplastic antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces verticillus. Binds to DNA, inhibits DNA synthesis and causes DNA scissions at specific base sequences. Needs to bind oxygen and a metal ion such as copper or iron to cleave DNA. Highly selective cleavage of RNA. Inducer and regulator of apoptosis in a variety of cells. Inhibits tumor angiogenesis. |
|
| Applications: |
Used as a transformed cell selection agent, especially for plant transformants |
